In our modern world, where electricity powers nearly everything we do, understanding how electrical systems distribute power is crucial. The Power Distribution Board (PDB) stands out as a crucial element within this setup This article delves into what a power distribution board is, its significance, and how it functions.
What is a Power Distribution Board?
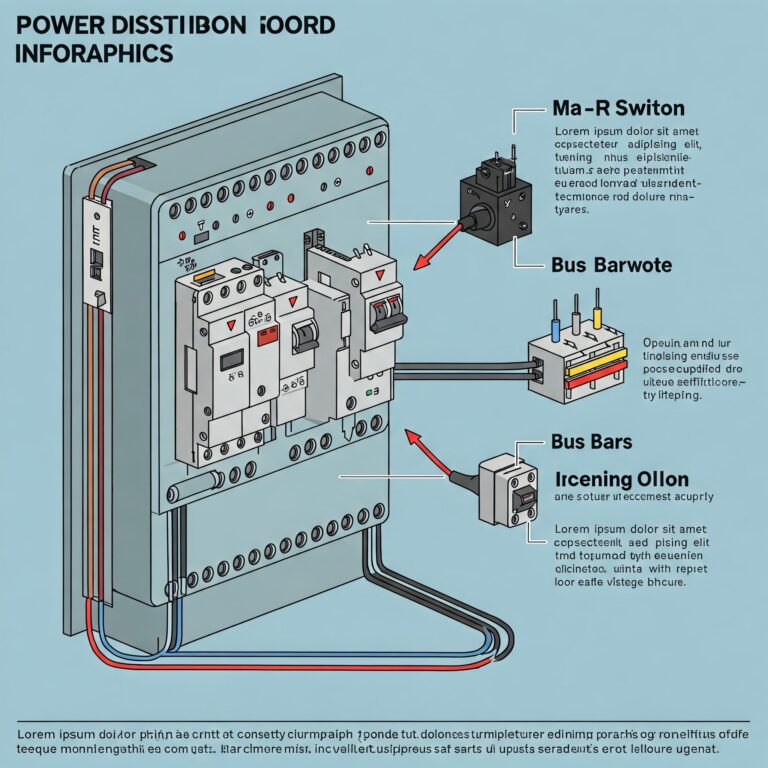
A Power Distribution Board, often referred to as a distribution board or panel, is a crucial part of an electrical system that distributes electrical power to various circuits within a facility. It acts as the central hub for electrical distribution, ensuring that power is routed safely and efficiently to different areas or devices.
Key Components of a Power Distribution Board

- Main Switch: This is the primary control switch used to turn the entire system on or off. It helps prevent overloads and protects the system from faults.
- Circuit breakers are protective mechanisms that automatically interrupt the electrical current when a fault occurs, such as during an overload or short circuit.. Once the problem is fixed, they can be switched back on
-
Bus bars are conductive strips or rods responsible for distributing electrical current across multiple circuits.
. They serve as the main conduit for electricity within the board.
- Incoming Supply Cables: These cables bring electrical power from the utility service or generator into the distribution board.
- Outgoing Circuit Cables: These cables carry the distributed power to different circuits or loads throughout the premises.
How Does a Power Distribution Board Work?

The operation of a power distribution board can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Receiving Power
The power distribution board (PDB) obtains electrical energy from the primary source, which can be either the utility grid or a backup generator. The incoming supply cables connect to the main switch within the board, allowing for power control.
2. Distribution via Bus Bars
Once the power enters the board, it travels through the bus bars. These bars are designed to handle high current loads and effectively distribute electricity to various circuits.
3. Circuit Protection
. When the current surpasses a safe threshold, the circuit breaker shuts off the power to that circuit by tripping This is a crucial safety feature that helps prevent electrical fires and equipment damage.
4. Power Delivery
The outgoing circuit cables carry the electricity to different loads, such as lighting, appliances, and machinery across the facility. The PDB ensures that each circuit receives the appropriate voltage and current, contributing to operational efficiency.
Importance of Power Distribution Boards

Safety
Efficiency
An effective distribution board optimizes power usage across various circuits, reducing energy waste. As a result, energy costs decrease and the efficiency of the electrical system improves
Scalability
Power distribution boards can be configured to support future upgrades or expansions Whether a business is growing or a facility is being upgraded, PDBs can be modified to handle additional circuits and loads, providing flexibility in electrical design.
Conclusion
Power Distribution Boards are fundamental to the safe and efficient distribution of electricity in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Understanding their components and how they work equips individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about their electrical systems. By prioritizing safety and efficiency, power distribution boards continue to be an essential element in our electrified world.